Download speeds and upload speeds sound similar on the surface, so what exactly is the difference between the two?
Before we explain, it’s important to note that many internet providers offer a range of download and upload speeds at different prices. However, not all providers and speeds are available in every location. Checking you internet availability by address can help you determine which ISPs and plans are accessible in your area. Some common examples:
- Xfinity internet (Cable)
- Earthlink internet (Fiber)
- Centurylink internet (DSL)
- Starlink internet (Satellite)
To help you sift through the noise, we’ll break down the definitions of each type of speed and help you figure out what you should be paying for.
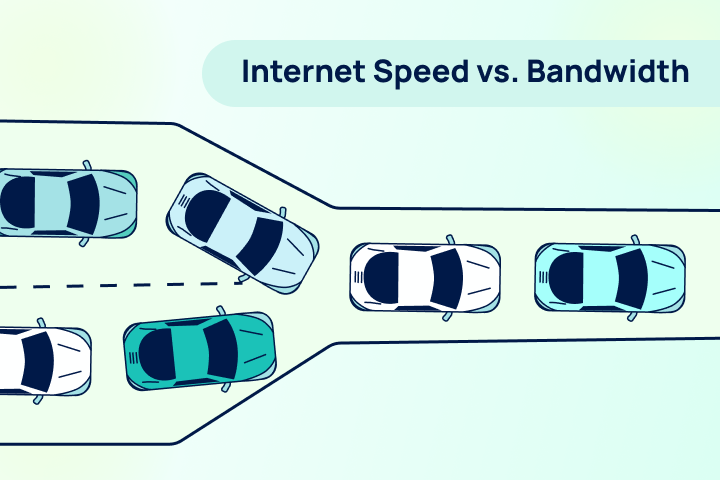
Bandwidth vs. Speed
It’s best to understand what you’re buying before starting your search. All internet plans focus on the amount of bandwidth you’ll receive from your provider. Bandwidth is measured by megabits per second (Mbps). So, when looking at a plan that says you’ll receive 25 Mbps, that is the maximum amount of data your internet connection can handle at one time. While a higher bandwidth increases your amount of data, it does not necessarily mean you’re getting better performance. More on that later.
Internet speed, on the other hand, is the rate at which data can be downloaded or uploaded on a given device. This is also measured in Mbps. Keep in mind that, when comparing internet plans, the speeds listed are only the maximum speeds you could possibly receive.
Think about a highway when comparing bandwidth and speed. Bandwidth represents the number of lanes on a highway. The more lanes on a highway, the more cars that can be on the highway at a given time. When there are fewer cars on the road, the cars move quickly. The more cars you add to the highway, the slower the cars move because the route becomes congested.
With bandwidth, the more users and devices you have on one connection, the slower your ability is to upload and download data. Basically, internet traffic is similar to real-life traffic.
It’s essential to consider the number of users and devices you will use in your home regularly. You want to be sure that you have enough bandwidth to accommodate your needs without compromising speed. You can get a sense of your current bandwidth speed using our internet speed test.
What is Download Speed?
Download speed refers to how quickly data is transferred from the internet to your device. This speed is crucial for most online activities, such as browsing the web, streaming videos, and downloading files. For example, if you enjoy watching movies in 4K, you’ll need a fast download speed to ensure smooth playback without buffering. Fiber-optic, cable internet, and select 5G internet providers offer the fastest download speeds among ISPs.
What is Upload Speed?
Upload speed is the rate at which data is sent from your device to the internet. This speed comes into play when you’re sending emails, uploading photos or videos, or participating in video conferences. If you’re a remote worker who frequently attends Zoom meetings or a content creator who regularly uploads large files, a slow upload speed can significantly impact your productivity and lead to frustration.
Symmetrical Speeds
Symmetrical speeds refer to an internet plan with the same upload and download speeds. Some internet plans offer symmetrical speeds, which means the download and upload speeds are the same. This feature is particularly important for users who heavily rely on upload-intensive tasks. For instance, a graphic designer who needs to upload large design files to clients or a YouTuber who regularly uploads high-quality videos would greatly benefit from symmetrical speeds.
Many providers prioritize download speeds over upload speeds because they’re typically used for more online activities like web browsing and gaming. When your download and upload speeds are different, they are called asymmetrical speeds.
If you are a remote worker or content creator that frequently uploads files to the internet, you will want to pay attention to this feature. Upload speeds can significantly slow down your workflow if they’re not fast enough.
How Much Speed Do I Need?
In general, internet plans can include speeds ranging anywhere from 1 Mbps to over 3000 Mbps. Anything above 25 Mbps is considered fast enough for modern applications, but speeds below 200 Mbps can be challenging for a large household. In households with multiple devices like streaming video or mobile gaming, opting for higher speeds can further enhance the experience by reducing interruptions and maintaining consistent performance. Check out the FCC’s recommendations on the right amount of bandwidth for your needs.
Take note of the speed your plan offers. Most plans offer asymmetric speeds, since more users consume content rather than upload it. So, download speeds are faster than upload speeds. Plans advertised as “5/1” mean that you’ll get 5 Mbps of download per 1 Mbps of upload.
Testing Your Internet Speed
If you’re unsure about your current internet speeds, you can easily test them using TestMySpeed.com. These tests will measure your download and upload speeds in Mbps. Compare your results to your internet plan’s advertised speeds and the FCC’s recommendations to determine if you have sufficient bandwidth for your needs.
Find how much Internet Speed do you need
Your household may want faster internet speeds.
<50 Mbps
Great for individuals to browse the internet, check email, and other basic browsing.
50-100 Mbps
Great for streaming Netflix, videos, and online meetings.
100-200 Mbps
Great for streaming high quality videos, fast downloads, video games, and multiple devices.
200+ Mbps
Great for doing almost anything at ultra fast speeds.
Understanding the difference between download and upload speeds is key to choosing the right internet plan for your household. By assessing your online activities and bandwidth requirements, you can ensure that you have the necessary speeds to support your daily needs. Remember, while higher speeds generally provide a better experience, it’s essential to strike a balance between performance and cost. With this knowledge in hand, you’re well-equipped to make an informed decision when selecting your next internet plan.